Wireless Networking
Wireless Networking
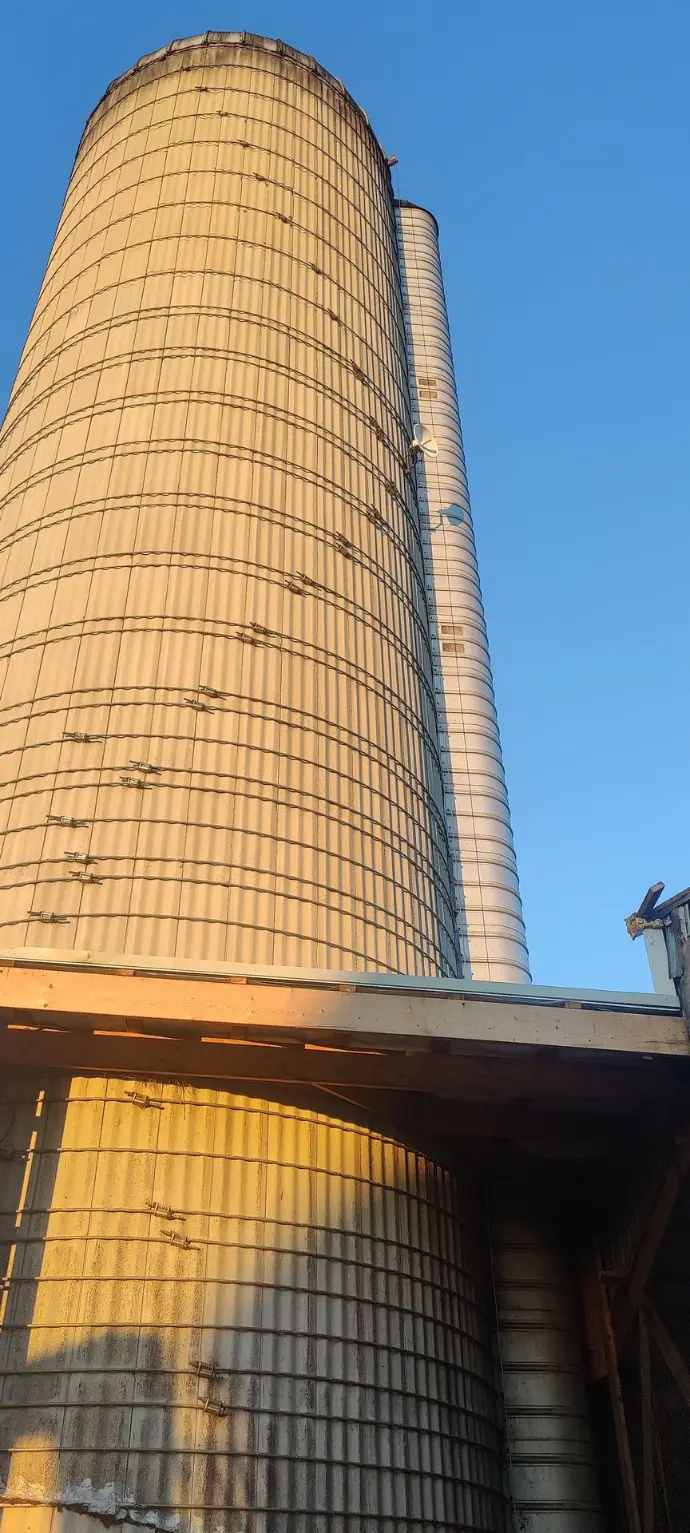
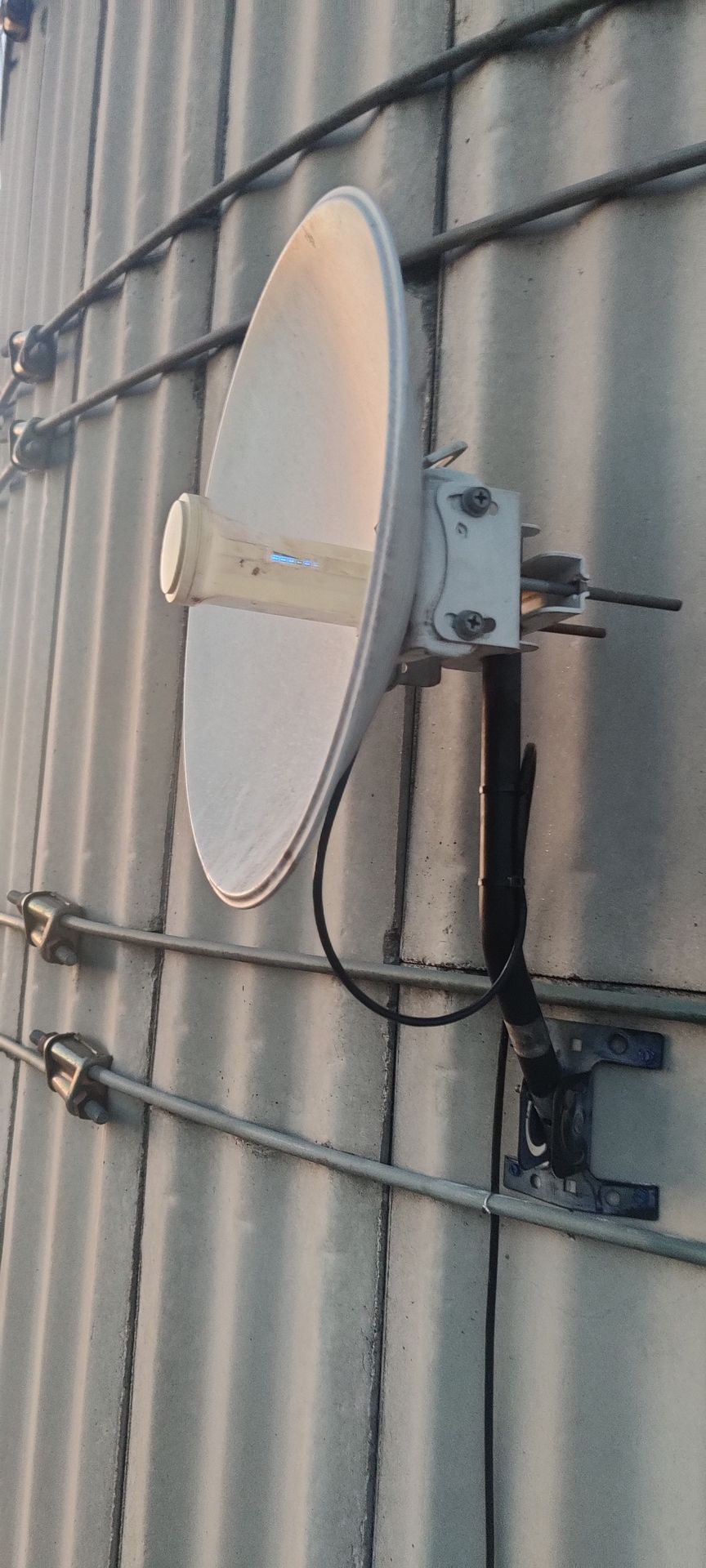
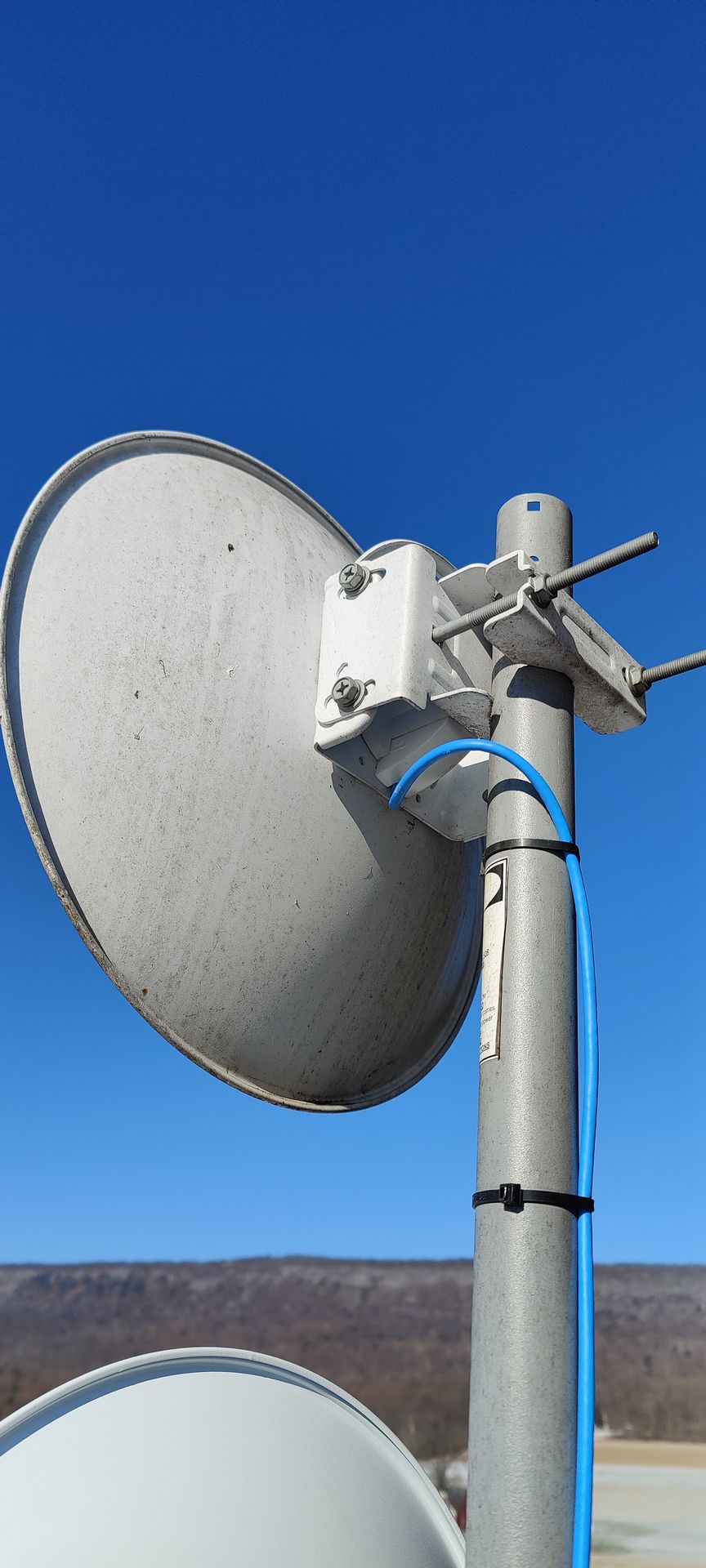
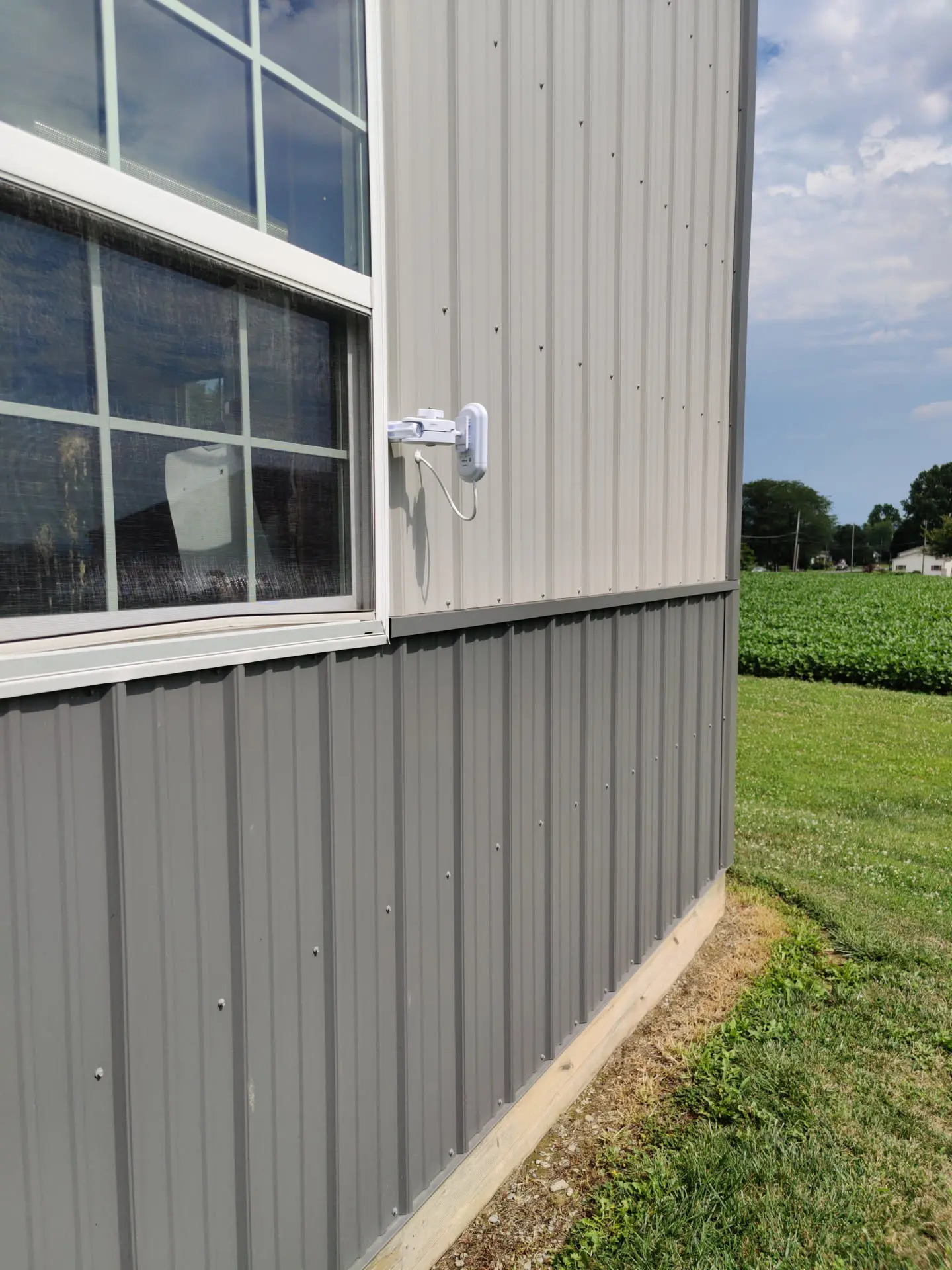
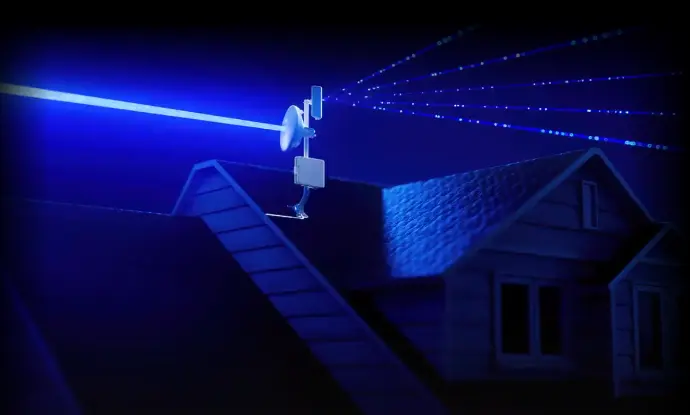
We offer long-range antennas which are commonly used in wireless communication systems, such as point-to-point and point-to-multipoint connections. Applications include wireless broadband, rural internet connectivity, and remote sensor networks.
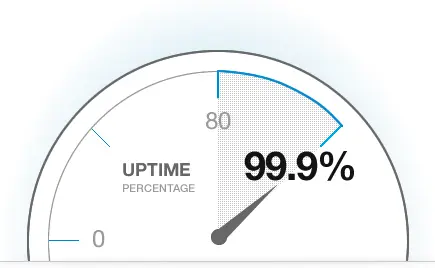
99% AVG UPTIME
Achieving and maintaining a 99% uptime is a significant goal for any system or service.

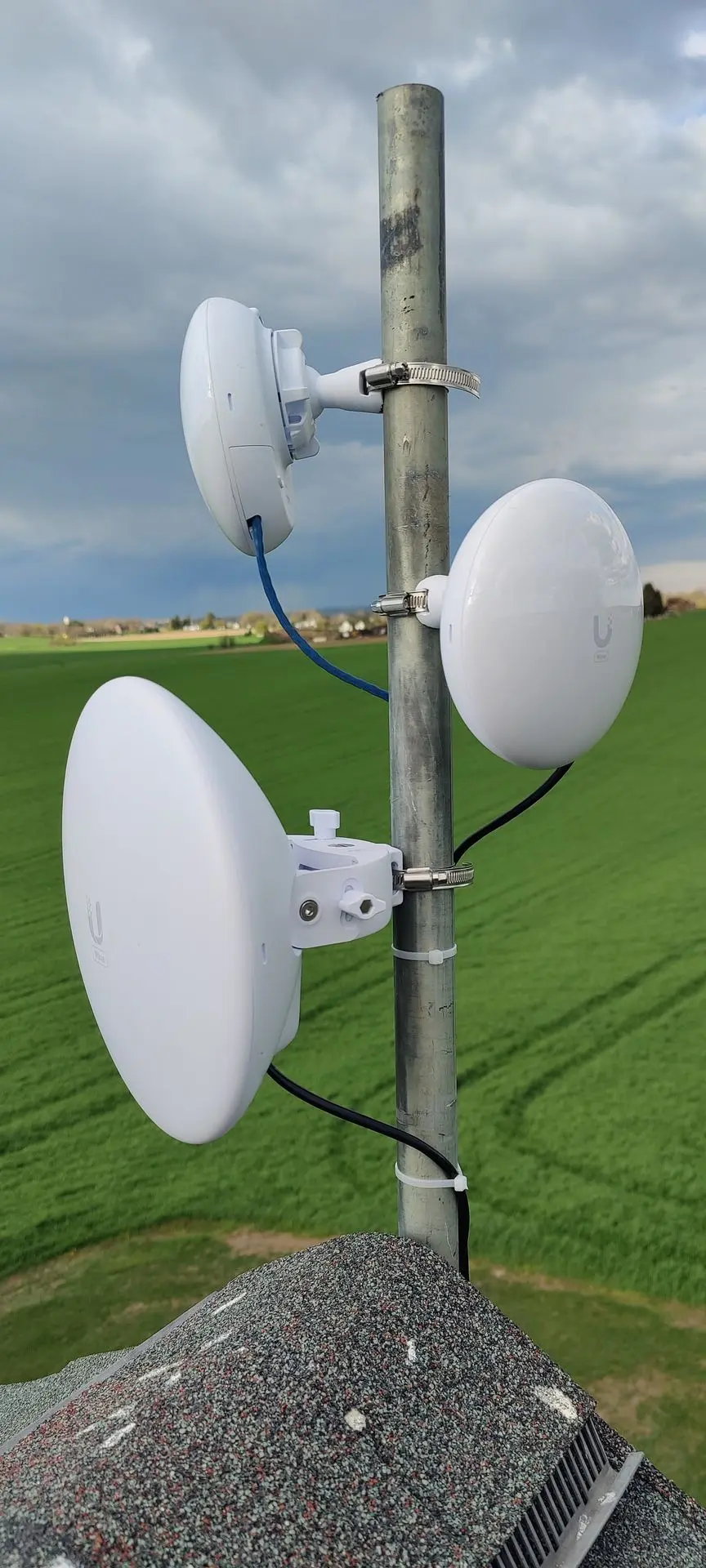
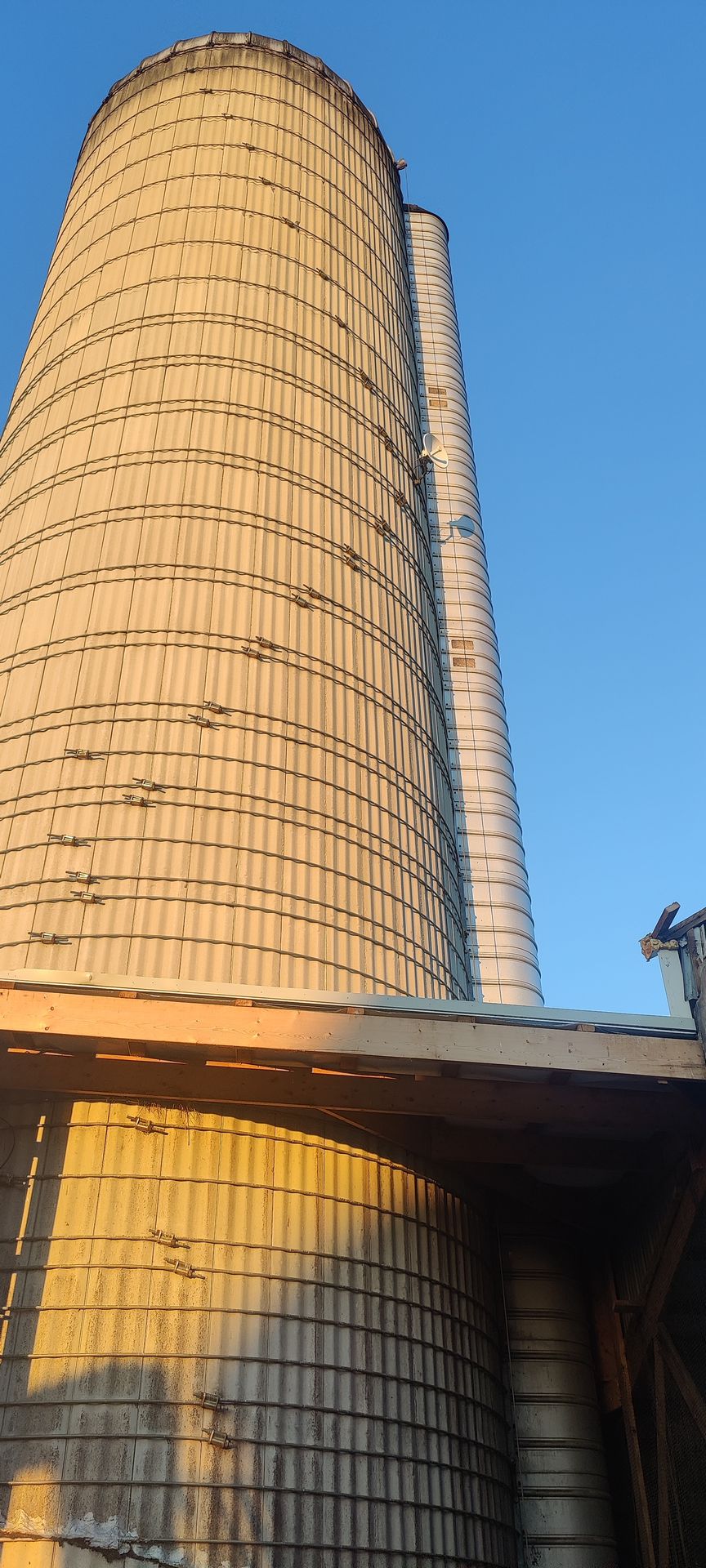
Over 100 Antennas
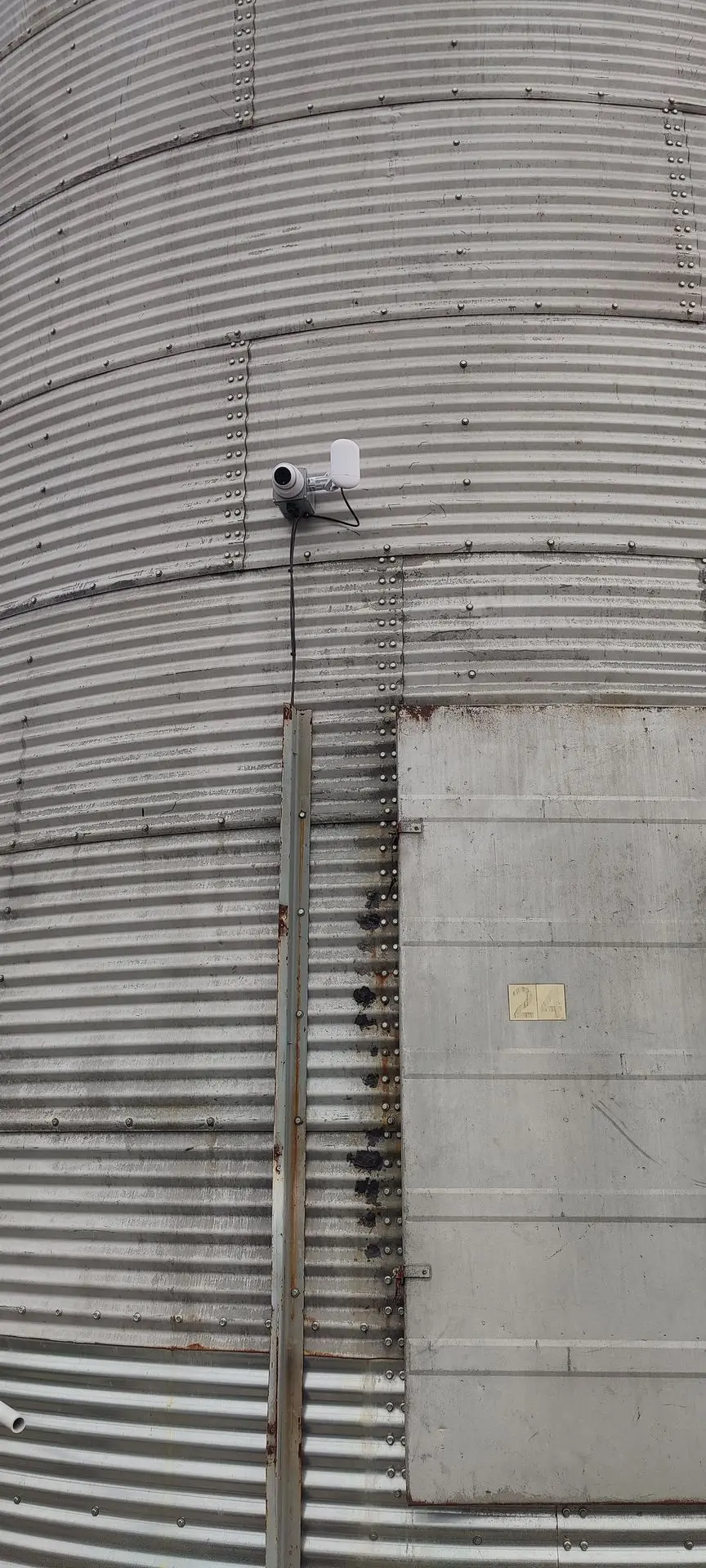
Over 100 antennas currently in operation. Whether it's for telecommunications, wireless networking, research, or another purpose, managing such a network involves considerations for optimization, maintenance, and ensuring reliable connectivity
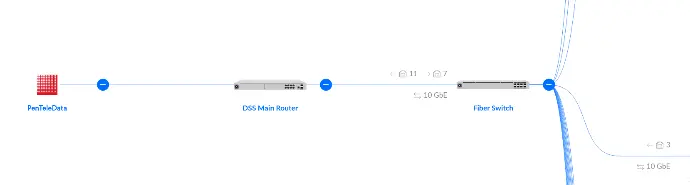
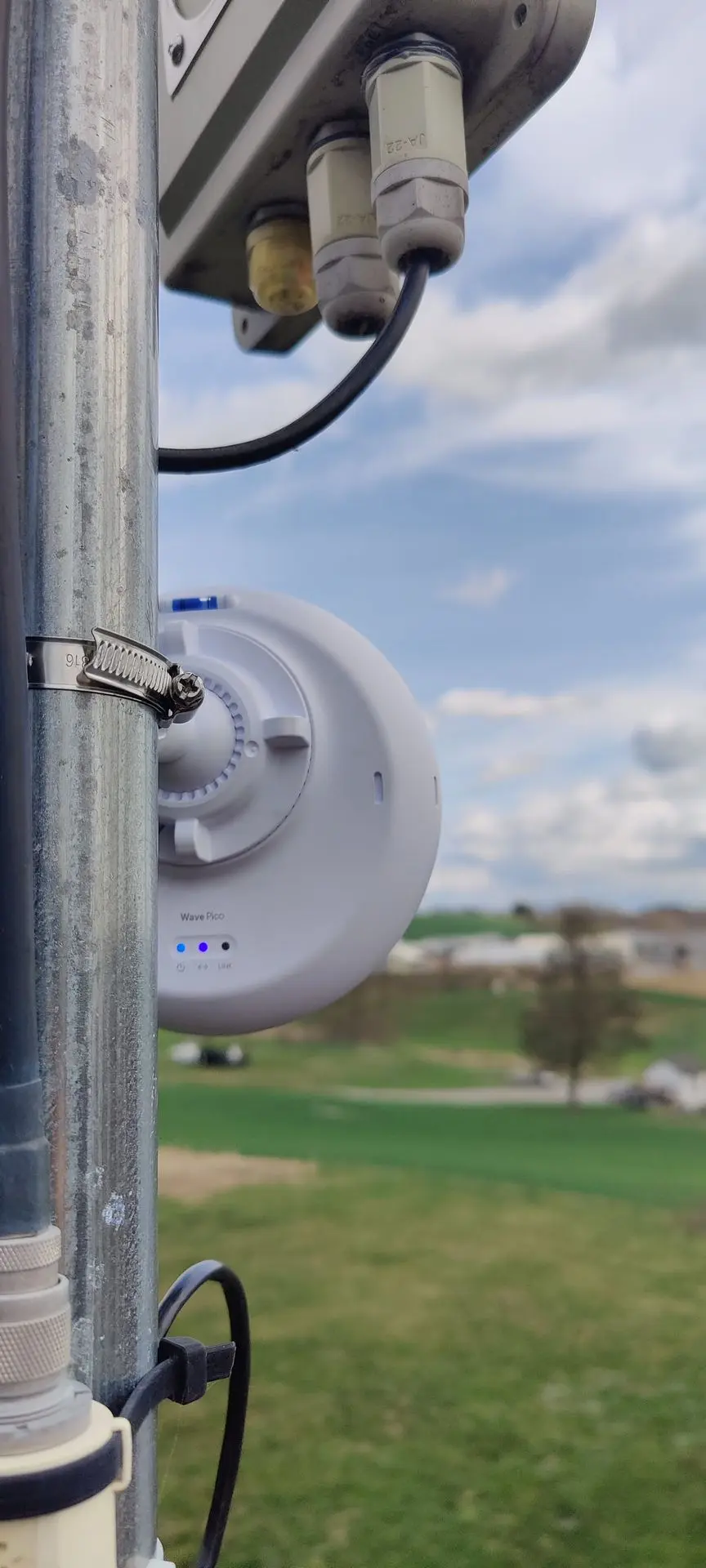
Remotely Managed
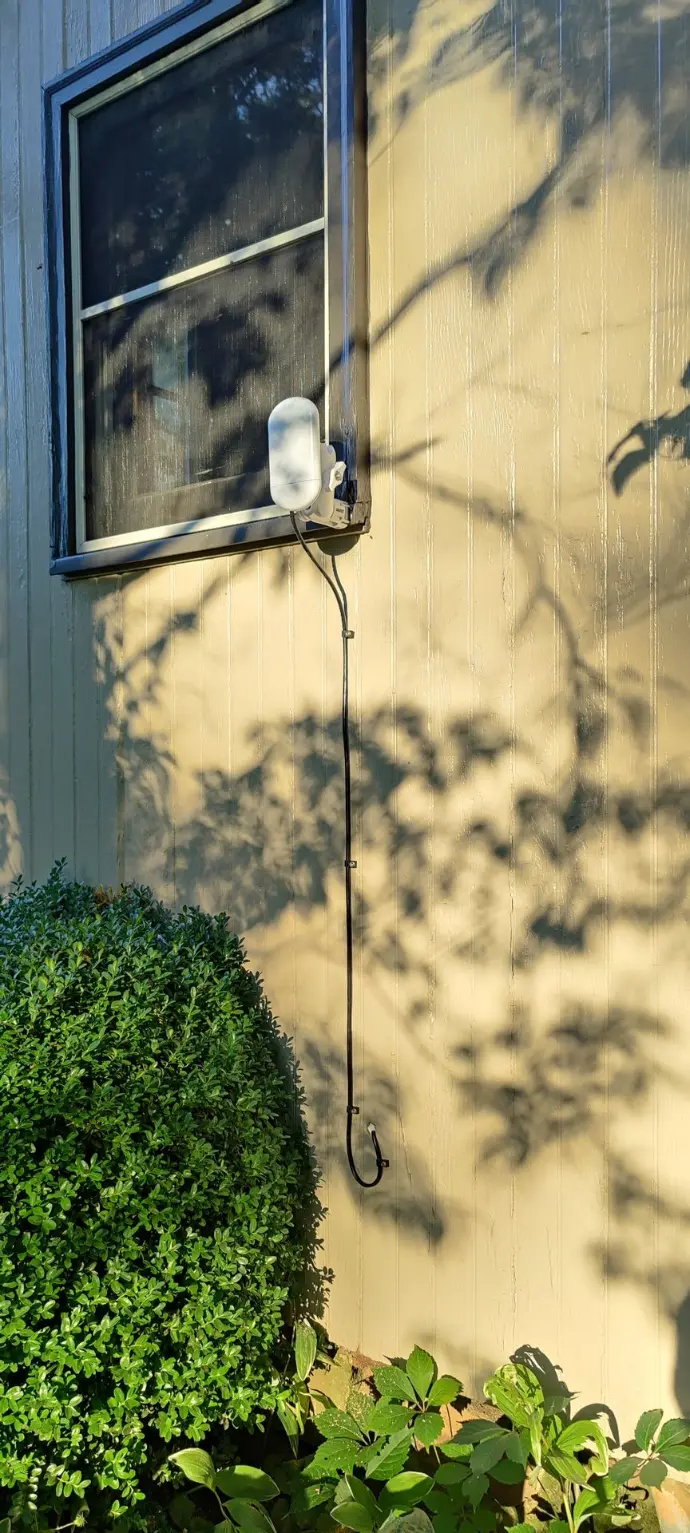
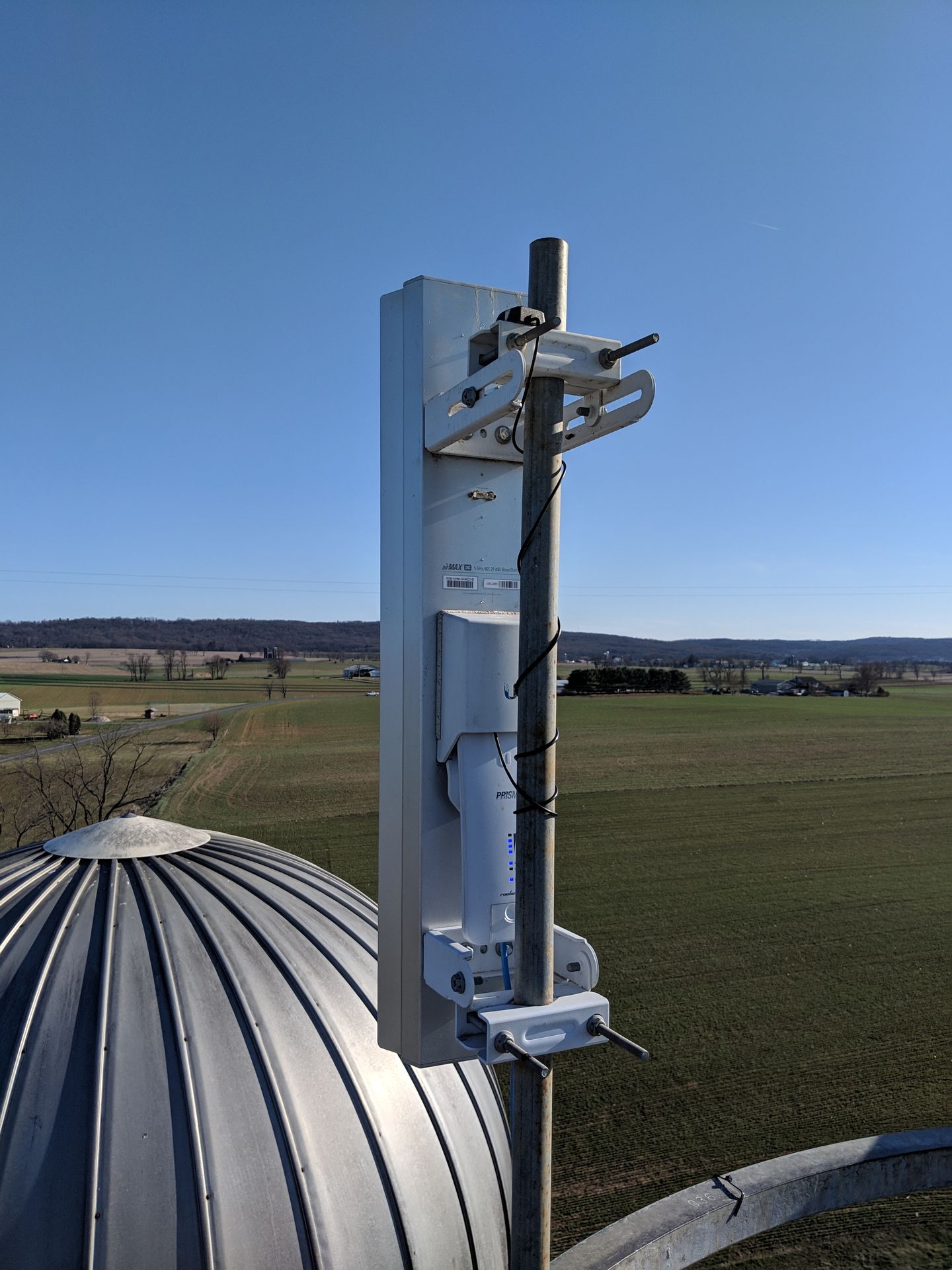
Remotely managed antennas that are monitored, configured, updated, and controlled remotely using advanced management and control systems. This capability allows for efficient operation, troubleshooting, and optimization of the antenna performance without requiring physical access to the antenna site.
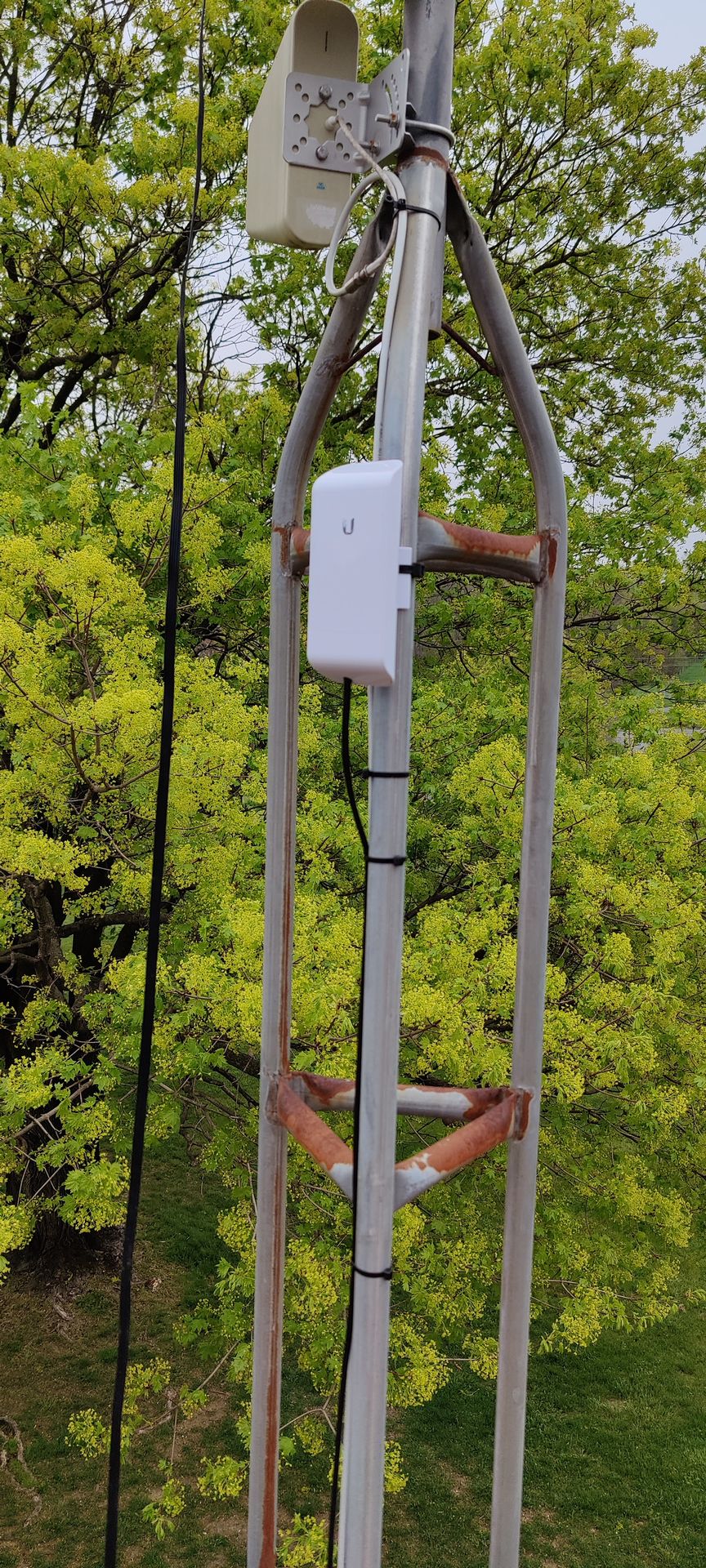
Omnidirectional Antenna: Is a type of antenna that radiates or receives radio-frequency (RF) signals uniformly in all directions, 360 degrees around its axis. Unlike directional antennas that focus signals in a specific direction, omnidirectional antennas provide a 360-degree coverage pattern
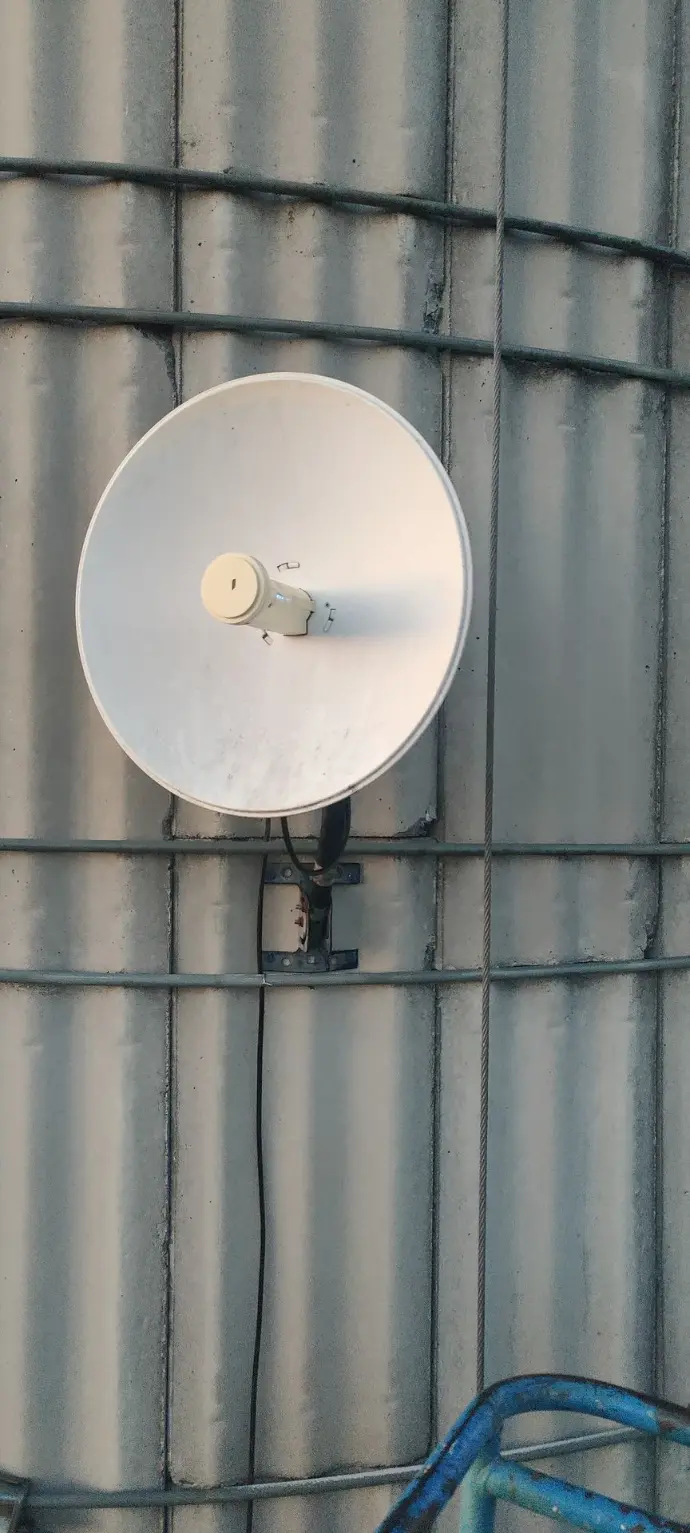
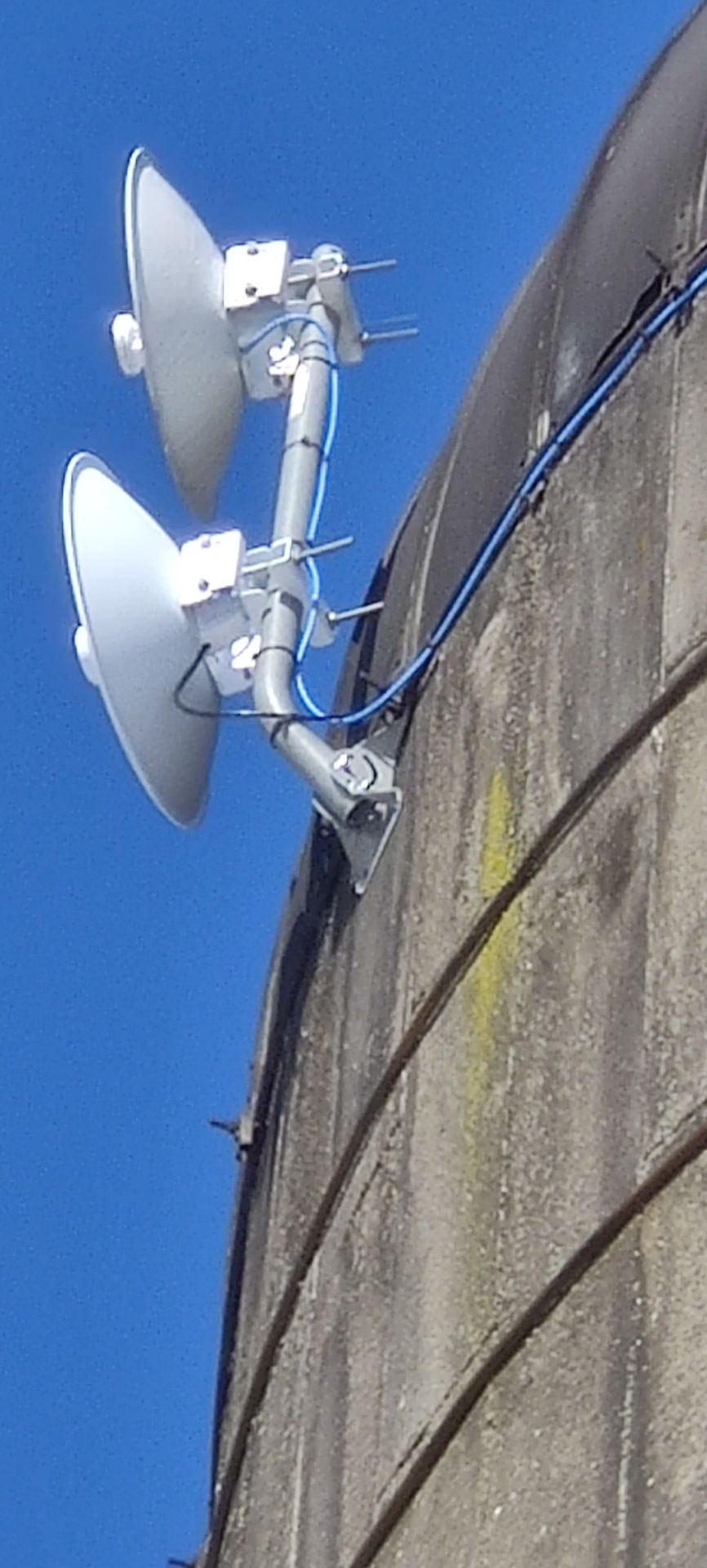
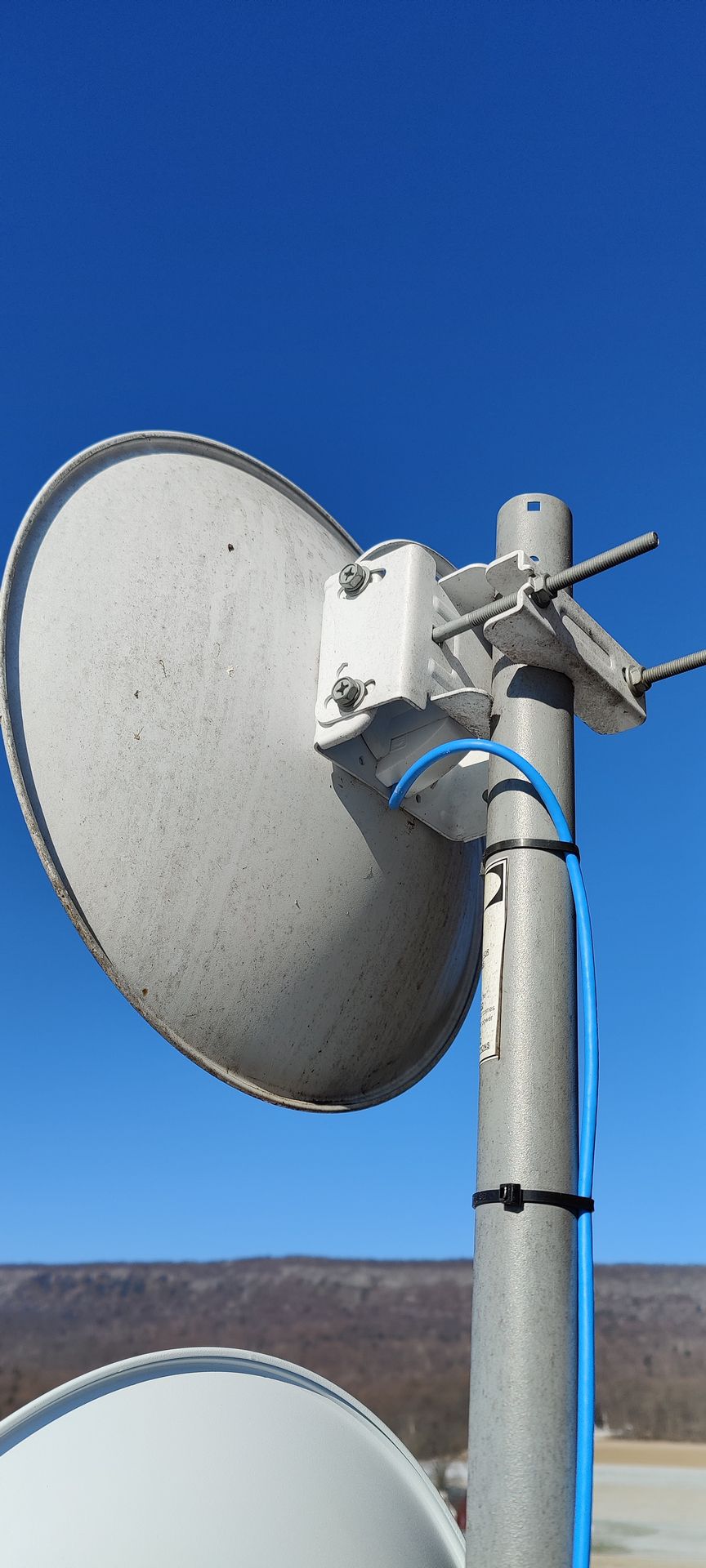
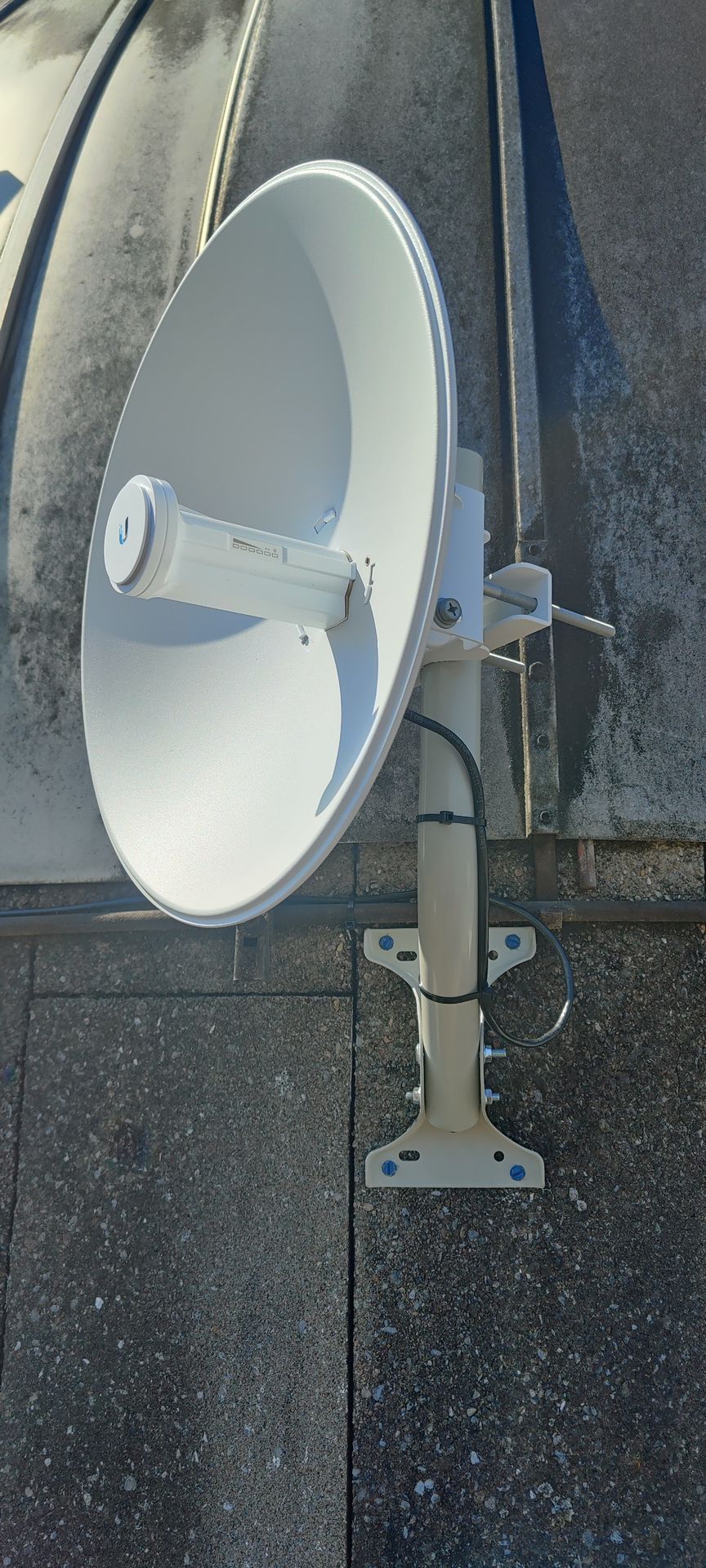
Directional Antennas: These focus signals in specific directions, providing increased range and signal strength for targeted communication.
Yagi Antennas: Known for their high gain and directionality, Yagi antennas are commonly used for long-range point-to-point links.
Long-range antennas are designed for specific frequency bands based on the communication requirements. Lower frequency bands (such as VHF and UHF) are often preferred for longer ranges due to better signal penetration and propagation characteristics.
Telecommunications: Long-range antennas play a crucial role in providing connectivity for remote areas, establishing communication links between base stations, and supporting telecommunication infrastructure.
Surveillance and Monitoring: Used in applications like border security, wildlife tracking, and environmental monitoring where long-range communication is essential.
Remote Sensing: Applications involving data transmission from remote sensors or devices in agriculture, environmental research, and industrial monitoring.
Long-range communication may require higher transmission power and amplification to overcome signal attenuation over distance. Amplifiers may be integrated into the antenna system to boost signal strength.
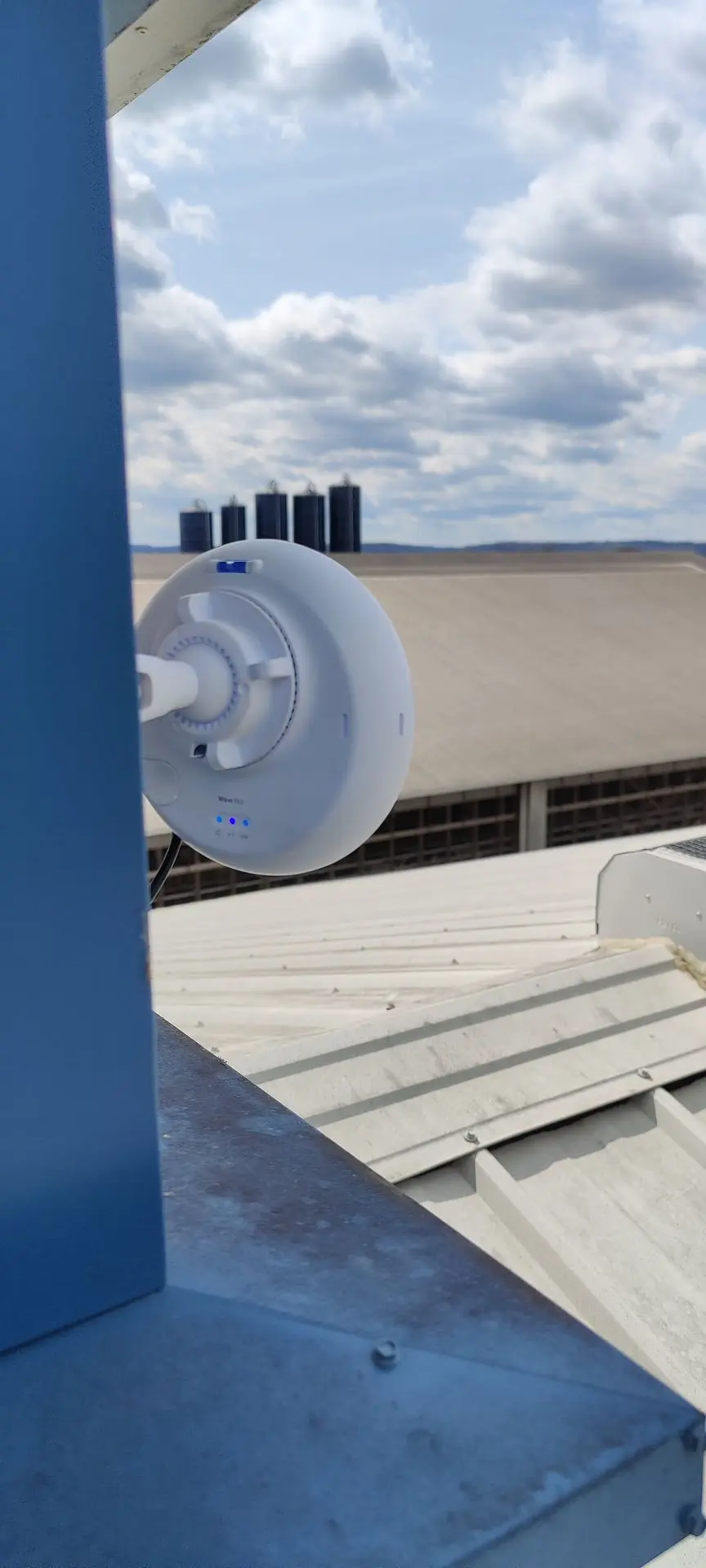
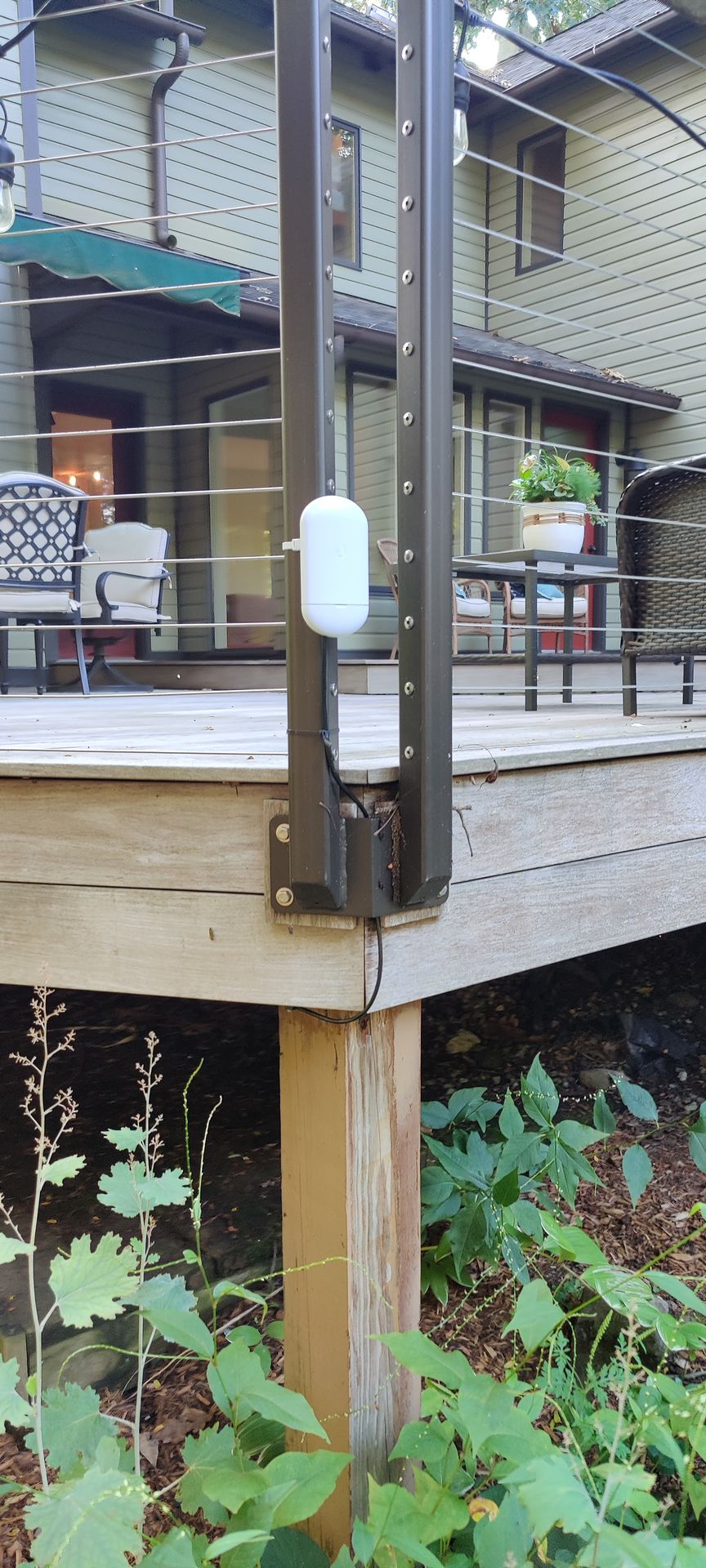
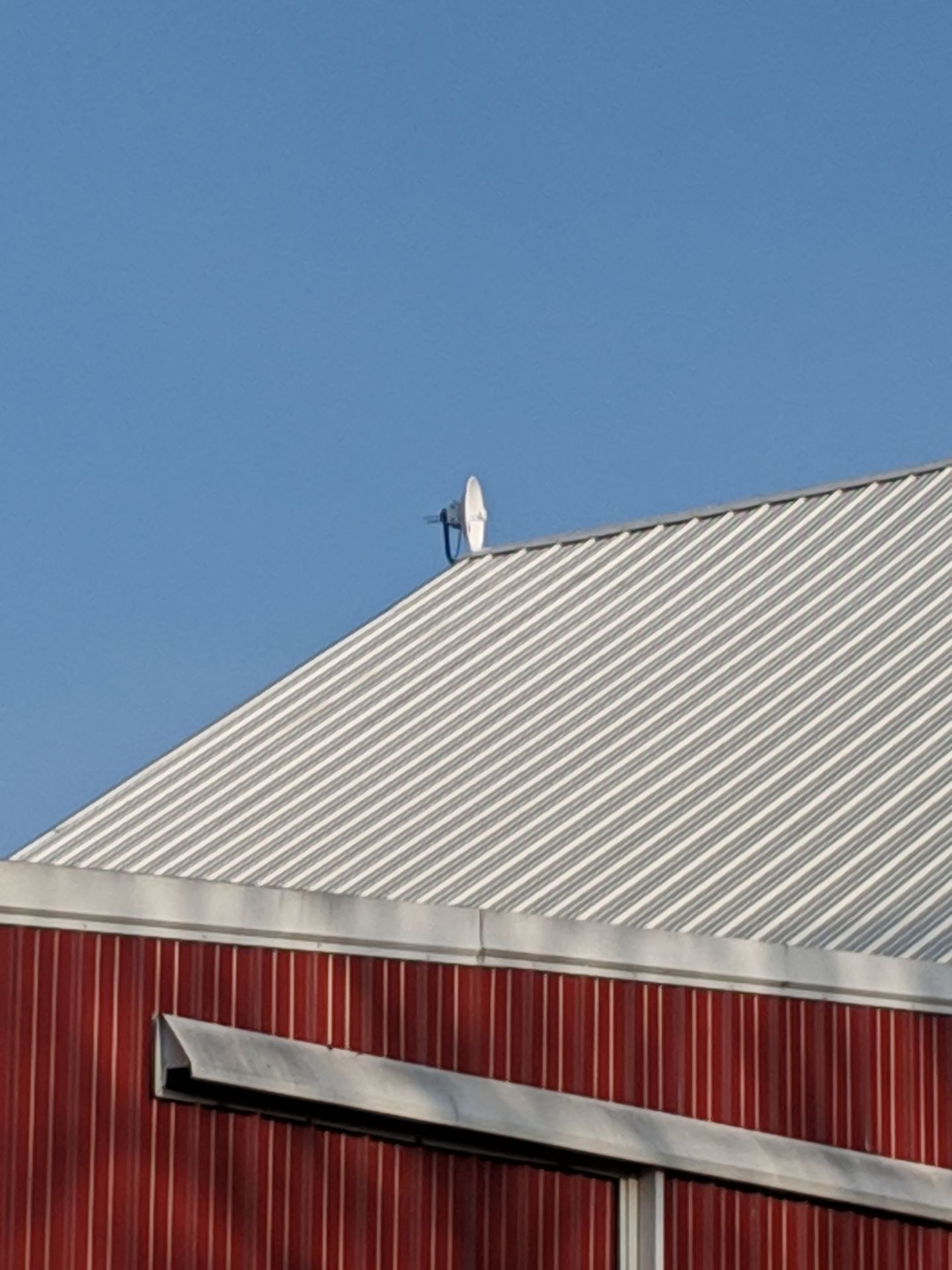
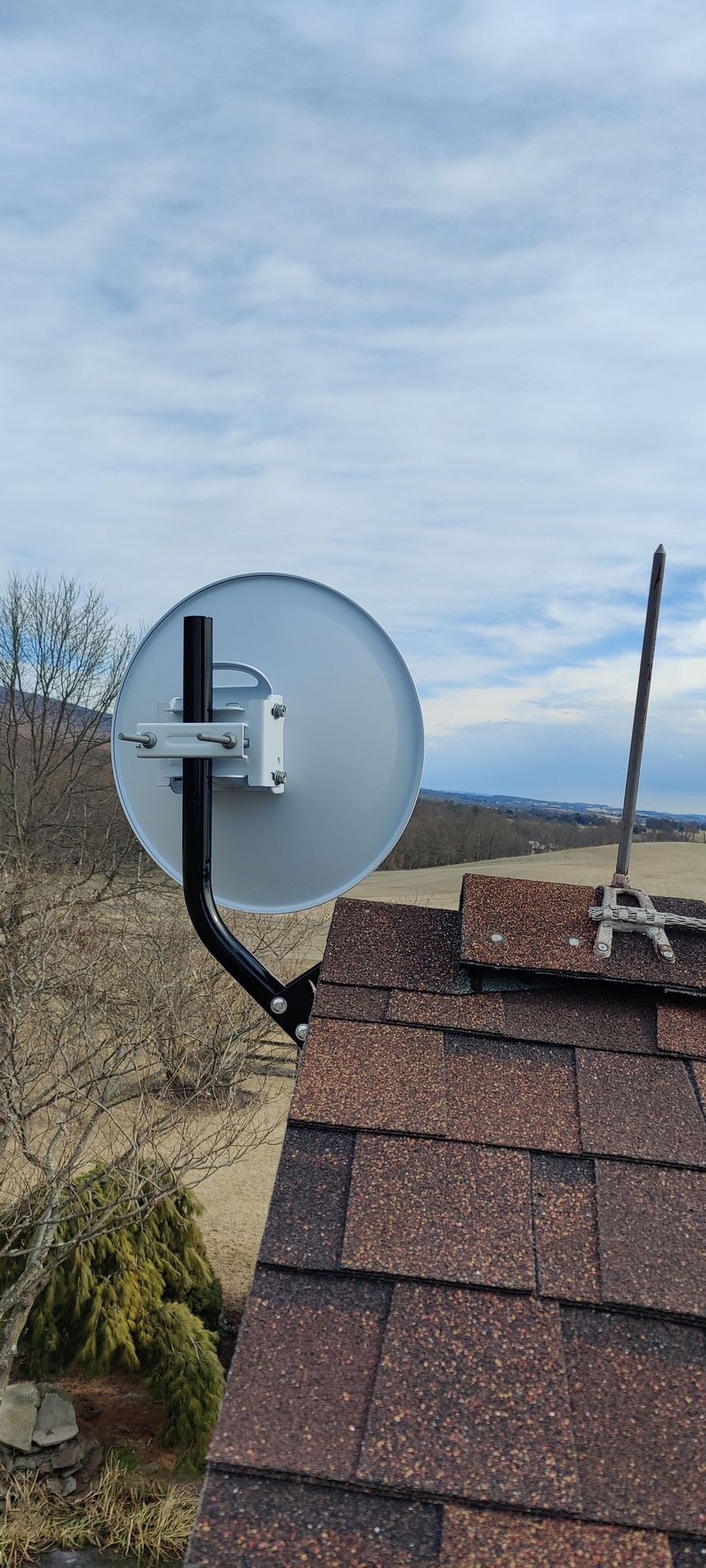
Long-range antennas are commonly employed in point-to-point communication links, connecting two fixed points over a considerable distance. This is prevalent in scenarios such as building-to-building connectivity or establishing links between communication towers.
The environment in which the antenna operates (urban, rural, mountainous, etc.) can impact its performance. Long-range antennas may need to be designed to withstand challenging weather conditions.
Compliance with regulatory standards and licensing requirements is essential, especially when operating in specific frequency bands and at higher power levels.
Long-range antennas are seamlessly integrated with communication systems, ensuring compatibility and efficient data transfer.





















